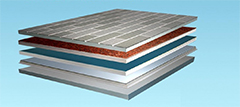
PRODUCT
MINMETALS EAST NEW MATERIAL